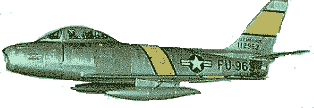
The Sabre first flew as the XF-86 in 1 October 1947, but it wasn't operational until 1948 as North American Aviation incorporated as much of the new jet technology captured from the Germans as was possible. Most important of which was the concept of the swept-back wing that enabled much higher speeds, approaching the speed of sound (Mach 1).It was first built as the FJ-1 Fury for the American Navy with a straight wing, but it was much slower, and therefore, less capable than the F-86. from the pilots perspective the major improvements were the ejector seat, powered controls, pressurised cockpits,and hard "bonedome" helmets. The seats and powered controls were required with the high speeds they were flying at, and a pressurized cockpit was a necessity flying and fighting from ground level to 40,000 ft. The major adversary they faced was the MiG-15 in Korea. Technically it should have been the Sabres falling to the ground in flames based on the flying abilities of the MiG-15. It generally had the edge on the Sabre, however, pilot training and willingness to engage in battle swung the pendulum way over to the United Nations (read Americans) side. They achieved a 15:1 kill ratio over their Chinese, Korean and Russian opponents. By the final stage of the Korean War Sabres were used in ground straffing as no opposition was encountered in the air. |
| Many thousands of Sabres were built in American, Australian, Canadian,
Italian and Japanese factories. They saw ide-spread service in the Korean
war of 1950-1953 and many were still in service with air forces outside
the USA in the 1970's. More than a dozen versions were built, for use as
tactical and interceptor fighters, all-weather fighters and fighter bombers.
Many pilots claimed that the Canadian built Canadair Sabre 6 with an Orenda
engine was the best aircraft of the series. Other variants were: the F-86H
had a J73 engine instead of the J47. A radar nose and a 'beard' air intake
characterized the F-86D, F-86K and F-86L single-seat all-weather interceptors.
The TF-86 was a longer trainer version and the RF-86 was a recce version;
bulges at the wing roots and under the cockpit housed the photographic
equipment. For the US Navy North American developed the FJ-2, FJ-3 and
FJ-4 Fury from the F-86.
|
| Technical Details
The initial variant the F-86 A flew in 1948 with the General Electric J47-GE-13 turbojet engine with 2,681 kg (5,910 lb) of thrust. The maximum speed was 687 mph (1,106 km/h) at sea level, although it was most fuel efficient at it's ceiling height of 40,000 ft. Effective combat range was 925 miles (1,490 km) with a pair of drop tanks mounted under the wings. Initially armament was six 0.5 in machine-guns in the nose and two 1,000 lb bombs instead of the drop tanks. With bombs the effective radius of operations was a mere 50 miles, with drop tanks it was more like 250. The Americans were committed to the 0.50 in machine gun when most air forces had gone with at least one cannon and several machine guns on jet fighters. Eventually it was equipped to fire two Sidewinder missiles, to drop two 453 kg (1,000 lb) bombs or fire eight 5 in rockets mounted under the wings. |
| The F-86F was brought out in 1952 and saw extensive service in Korea. It was powered by the G.E. J47-GE-27 turbojet engine. The major improvement was to increase the maximum speed slightly to (1118km/h) The ceiling was (15200m). Armaments were unchanged. The F-86D flew in 1953 as an all-weather interceptor and did not see service in Korea. It was powered by the improved G.E. J47-GE-17 with 3026kg of thrust. Maximum speed was boosted to (1,115 km/h). The ceiling was unchanged. Armaments were changed to a set of 24 70 mm rockets mounted in a retractable box, aimed and fired by computer. The guns were later returned. |
My thanks to for all the above text to Canadian Aces Home Page
Copyright acknowledged
Image From:
Headquarters AETC
LG Aircraft Images Home Page
Details From:
The Military
Aircraft Database by Emmanuel Gustin.
Great Fighting Planes by Alan Austin and Anthony Dicks
| Ben Halligan Front Page | 2 Cavalry Squadron Front Pages |