Firewall
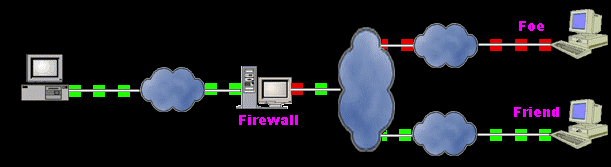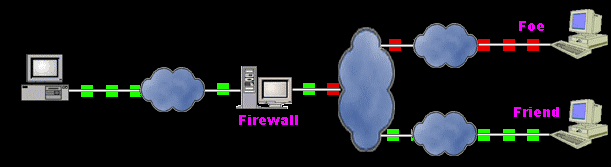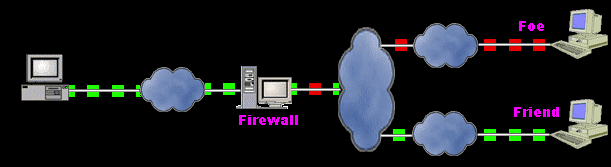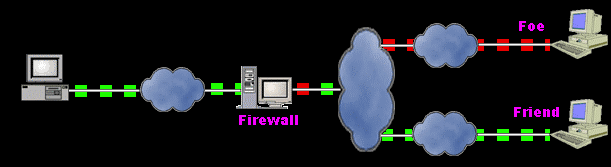
An illustration of a firewall blocking a foe's transmissions
General
Firewalls are systems that establish access control policies among networks.
They can block information from entering a network or from getting out
of that network, they can permit different users to perform different kinds
of operations, according to the user's authorizations.
There are several kinds of firewall implementations which enable each
company to decide what exaclly are the characteristics of the security
policy that would best fit its special demands.There are two general types
of firewalls: Packet Level Firewalls, which examine
packets and decide according to filtering rules whether to pass them
to the network. and Application Level Firewalls, which monitor specific
applications protocols.
Characteristics
-
Filtering Router - Since firewall is actually a filter which decides which
packets are authorized to reach a local network from the outside network
and which are considered hostile, the simplest way to implement a firewall
is by discarding packets that came from certain IP addresses while allowing
those packets, whose source IP address is in a predefined list, to access
the network. The problem with such a simple firewall is that it is very
easy to forge a source IP address. Therefor, this kind of firewalls are
not commonly used.
-
Proxy Server - In order to achive a better security features, a firewall
can use an application level gateway. The gateway is located between two
firewalls (routers), each on the other side of the gateway. This firewalls
will deliver only information which target is the gateway or information
whose source is the gateway. This way, only information that was sent by
a local user to the gateway can be reached by an external user and local
user which wishes to receive information from the external network must
first get loging permissions from the gateway which would fetch the information
according to the company's security policy.
-
Circuit Level Proxy - A circuit level
proxy verifies, according to predefined secuirty files, whether a
certain IP datagrams are "safe" to deliver through a firewall. After we
establish connection it is resposible to deliver packets from and to an
external network from a user application.
-
Application Level Proxy - The main
difference between Application Level Proxy and Circuit Level Proxy or Filtering
router is its ability to "understand" applications specific information
structure. This way the Application Level Proxy can examine application's
flow of information and decide whether to allow specific application level
requests for information, or requests to change information and not only
to decide according to "external" charateristics of the information packets.
In order to achive such security level, the firewall must "know" each user
application. The main problem is that the Application Level Proxy is not
transparent to the user which must take into consideration that the
information may be filtered due to context problems. Another problem is,
of course, that applications communication protocol should be supported
by the firewall.
Related topics