
|
|

The Microscope
History:
Galileo invented one of the very first microscopes. It was a lot different to the one that we use today. It didn't use any type of energy, for example. Microscopes that we use today are run on electricity. When Galileo invented the microscope, scientists were able to learn more about germs and diseases. But for microscopes, doctors would not know the causes of illnesses..![]() They were first used during the early seventeenth century
They were first used during the early seventeenth century
![]() We don't know who invented it because several different types were used during the time
We don't know who invented it because several different types were used during the time
![]() Many discoveries were made by Robert Hooke and Leeuwenhoek with primitive microscopes
Many discoveries were made by Robert Hooke and Leeuwenhoek with primitive microscopes
![]() In the olden days they only used one eyepiece
In the olden days they only used one eyepiece
![]() They also drew what they saw.
They also drew what they saw.
![]() These microscopes had an oil light which was concentrated into a bright spot with a ball filled with water.
These microscopes had an oil light which was concentrated into a bright spot with a ball filled with water.
![]() A little later on they reflected light from the sun or a light bulb with a mirror to shine up into the microscope.
People in ancient times knew that a drop of water that fell onto a grain of sand or small insect made the object it fell on look larger than it actually was. Seneca (4 B.C.- 65 A.D.), a Roman philosopher, observed that 'letters, though small and indistinct, are seen enlarged and more distinctly through a glass globe filled with water'. The first person to explain why this happens was Ptolemy, a Greek astronomer who lived in the second century A.D. He said that light was bent (or refracted) because it changed speed as it moved from one substance to another.
A little later on they reflected light from the sun or a light bulb with a mirror to shine up into the microscope.
People in ancient times knew that a drop of water that fell onto a grain of sand or small insect made the object it fell on look larger than it actually was. Seneca (4 B.C.- 65 A.D.), a Roman philosopher, observed that 'letters, though small and indistinct, are seen enlarged and more distinctly through a glass globe filled with water'. The first person to explain why this happens was Ptolemy, a Greek astronomer who lived in the second century A.D. He said that light was bent (or refracted) because it changed speed as it moved from one substance to another.
 Present:
Present:
![]() They now use electric lights instead of a flame or mirrors
They now use electric lights instead of a flame or mirrors
![]() They have two eye pieces so your eyes don't get tired
They have two eye pieces so your eyes don't get tired
![]() Instead of drawing they use cameras
Instead of drawing they use cameras
![]() They sometimes use digital cameras which can be sent to different places with computers
They sometimes use digital cameras which can be sent to different places with computers
What microscopes are used for:
![]() Microscopes are used for looking at blood cells, bacteria and viruses - and tiny creatures.
Microscopes are used for looking at blood cells, bacteria and viruses - and tiny creatures.
![]() They are used for looking at crystals but you can't see them with ordinary microscopes because they are clear so you have to get cellophane sheets so they become coloured.
They are used for looking at crystals but you can't see them with ordinary microscopes because they are clear so you have to get cellophane sheets so they become coloured.
![]() Sometimes they use a special microscope for doing operations. This is called microsurgery.
Sometimes they use a special microscope for doing operations. This is called microsurgery.
![]() Microscopes are also used to examine microchip to make sure the don't have any faults.
Microscopes are also used to examine microchip to make sure the don't have any faults.
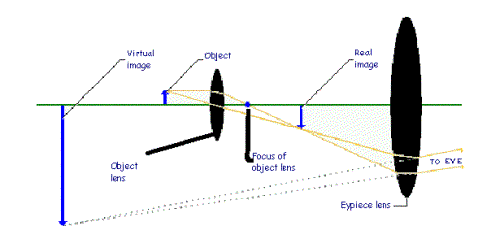 How microscopes work:
How microscopes work:
![]() The main parts of a microscope are the eyepiece, optic lens and a light source
The main parts of a microscope are the eyepiece, optic lens and a light source
![]() The microscope has a stage for holding the glass slide or object
The microscope has a stage for holding the glass slide or object
![]() The stage is move up and down to move the object into focus
The stage is move up and down to move the object into focus
![]() Underneath the stage is the a lens called the condenser which controls and focuses the light coming up
Underneath the stage is the a lens called the condenser which controls and focuses the light coming up
![]() The eyepieces usually have a magnification of ten
The eyepieces usually have a magnification of ten
![]() A microscope may have up to six objective lenses but most microscopes only have four.
A microscope may have up to six objective lenses but most microscopes only have four.
![]() These vary from ten too one hundred magnification
These vary from ten too one hundred magnification
![]() For some microscopes oil is needed for some of the objectives to get the best image
For some microscopes oil is needed for some of the objectives to get the best image
The Telescope
Nobody is quite sure who invented the telescope. In 1608, a Jacob Adriaanzoon applied for the rights to sell an instrument to sell that made distant objects appear larger. He used both concave and convex lenses at the ends of a tube to magnify objects. In 1609, Galileo designed his own telescope and made many discoveries in space - getting himself into a lot of trouble with the Church of the time.
In 1610, Galileo discovered Saturn's rings. They looked quite strange when he saw them! He kept notes of everything he saw and wrote of Saturn "Saturn is not a single star, it is a composite of three". Every night, Galileo studied Saturn, until one day he realized that Saturn orbits around the sun - just like the Earth. He later went on to discover that Saturn had foour moons. He named the moons after the Grand Duke of Tuscany's family (Medici). He called them thye Medicean moons.
Many people didn't believe Galileo's discoveries at first, until they were finally proven.