Objective
Number
| 1. |
Place value. To explore and identify place value in whole
numbers from 0 – 999.
Example 1: 342
Example 2: 913
|
| 2. |
To read, write and order three digit numbers.
Example 1: What is the next number after 499? ; Example 2: Put these numbers in
ascending order – 421, 241, 142 and 214
|
| 3. |
To round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or nearest hundred.
Example 1: 26, 13, 35; Example 2: 342, 258 and 850
|
| 4. |
To explore and identify place value in decimals to one place
of decimals.
Example 1: 0.3 ; Example 2: 496.7
|
Operations
| 1. |
Add and subtract without and with renaming within 999.
Example 1: 946 – 225; 400 + 120 +
366; Example 2: 401 – 234 ; 713 +
94 + 109
|
| 2. |
Know and recall addition and subtraction facts
Addition and subtraction tables to be taught; drills and patterns to be
taught as oral work
|
| 3. |
Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction
(single step and multi-step)
Example 1: A farmer had 104 sheep. He bought 69 sheep. How many has he then?
Example 2: A farmer had 230 hectares. He sold 95 hectares. How many hectares has
he then?
Example 3: There are 157 boys attending a school. There are 16 more girls. How
many pupils in the school?
Example 4: A milkman has 402 cartons, He sold 27 to one shop and 16 to another
shop. How many has he left?
Teaching strategies for problem solving
|
| 4. |
Develop an understanding of multiplication as repeated
addition and vice versa.
Example 1: 2 +2 +2 = ;
Example 2: 3 x 2 =
|
| 5. |
Explore, understand and apply the zero, commutative and
distributive properties of multiplication.
Example 1: Tick the correct answer : 5 x 0 = 5, 1, 5.
Example 2: 5 x 2 = x 5
Example 3: 5 x 4 = (3 x 4) + (___ x
4)
Example 4: 7 x 14 = (3 x 14) + ( ____ x
14)
|
| 6. |
Develop and / or recall multiplication facts within 1000
counting in 2’s, 3’s, 4’s etc
|
| 7. |
Multiply a one digit or two digit number by 0 – 10.
Example 1: 13 x 3; Example 2: 25 x 6; Example
3: 24 x 7; Example 4 : 99 x 9 (this is the greatest level of demand at this
standard)
|
| 8. |
Solve and complete practical tasks and problems involving
multiplication of whole numbers.
Example 1: How many days in 9 weeks. Example
2: There are 47 crayons in a box. How many in 8 boxes? Example 3: A farmer has
52 sheep. Another farmer has 4 times as many. How many sheep have they
altogether?
|
Division
| 9. |
To develop an understanding of division as sharing and as
repeated subtraction, without and with remainders.
|
| 10. |
To develop and / or recall division facts within 100
|
| 11. |
To divide a one digit number or two
digit number by a one digit number, with or without remainders.
Example 1: 20 ÷ 4; Example 2: 35 ÷ 5; Example 3: 28 ÷ 3
Example 4: 85 ÷ 4; Example 5: 97 ÷ 5; Example 6: 61 ÷ 3
|
| 12. |
Solve and complete practical tasks and
problems involving division of whole numbers.
Example 1: 81 marbles were shared equally among 9 children. How many did each
get?
Example 2: How many boxes each containing 6 eggs can be filled from a container
that holds 5o eggs? How many eggs will be left over?
Example 3: How many bags containing 7 balloons can be made from 43 red balloons
and 41 green balloons?
|
Strand Unit
Fractions
| 1. |
Identify fractions and equivalent
forms of fractions with denominators 2, 4, 8 and 10.
Example 1: What part is shaded ?
Example 2: Shade 1/10 of this figure.
Example 3: Shade 5/8 of this figure.
Example 4: What fraction is shaded ?
|
| 2. |
To compare and order fractions with
appropriate denominators and position on the number line.
Example:
|
| 3. |
To calculate a fraction of a set
using concrete materials
|
Shade ¼ |
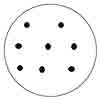
|
|
| 4. |
To develop an understanding of the
relationship between fractions and division
Example 1: ¼ of 32 =
Example 2: 1/8 of 64 =
Example 3: 32 ÷
4 =
Example 4: 64 ÷
8 =
|
| 5. |
To calculate a unit fraction of a
number and calculate a number, given a unit fraction of a number.
Example 1: ¼ of a number =3. What is
the number?
Example 2: 1/10 of a number =9. What is
the number?
|
| 6. |
To solve and complete practical tasks
and problems involving fractions.
Resources needed for practical tasks.
|
Strand Unit
Decimals
| 1. |
Identify 1/10’s and express in decimal
form
Example 1:
|
| 2. |
Order decimals on the number line
Example
|
| 3. |
Solve problems involving decimals
|
Algebra
Unit, Number Patterns and Squares
| 1. |
Explore, recognise and record patterns in number
|
| 2. |
To explore, extend and describe arithmetic and geometric
sequences.
Example 1: 1, 5, 9, 13, __, ___.
Example 2: 81, 27, 9, __
|
| 3. |
Use patterns as an aid in the memorisation of number facts.
|
Resources: Excel number patterns; 100 squares
Assessment: Informal
Strand Unit
Number Sentences
| 1. |
Translate an addition or subtraction number sentence with a
frame into a word problem.
Example 1: 3 + 7 = . Mary has three sweets. She gets seven more. How many
has she now?
Example 2: 900 - ______ = 460. Make up a problem.
|
| 2. |
Solve one step number sentences.
Example 1: 400 - _______ = 350
Example 2: 810 + 23 =
|
Strand Unit
Shape and Space
| 1. |
Identify, describe and classify 2d shapes (square, rectangle,
triangle, hexagon, circle, semi-circle, oval and irregular shapes.
Informal assessment – match word to shape
|
| 2. |
Explore, describe and compare the properties (sides, angles,
parallel and non-parallel) of 2D shapes.
Assessment: How many sides has a ______?
|
| 3. |
Construct and draw 2D shapes using templates, stencils,
geo-strips and geo-boards
|
| 4. |
Combine, tessellate and make patterns with 2D shapes
Use computer software
|
| 5. |
Identify the use of 2D shapes in the environment.
Assessment: Draw house / signs
|
| 6. |
Solve and complete practical tasks and problems involving 2D
shapes.
|
Strand Unit
3D Shapes
| 1. |
Identify, describe and classify 3D shapes, including cube,
cuboid, cylinder, cone, sphere, triangular prism and pyramid.
|
| 2. |
Explore, describe and compare the properties of 3D shapes
|
| 3. |
Explore and describe the relationship of 3D shapes with
constituent 2D shapes.
|
| 4. |
Construct 3D shapes
|
| 5. |
Solve and complete practical tasks and problems using 2D and
3D shapes.
|
Strand Unit
Symmetry
| 1. |
Identify line symmetry
|
| 2. |
Identify and draw lines of symmetry in 2 D shapes
|
Strand Unit
Lines and Angles
| 1. |
Identify, describe and classify vertical, horizontal and
parallel lines
|
| 2. |
Recognise an angle in terms of rotation
|
| 3. |
Classify angles as greater than, less than or equal to a
right angle
|
| 4. |
Solve problems involving lines and angles
|
Strand Unit
Length
| 1. |
Estimate, compare, measure and record lengths of a wide
variety of objects using appropriate metric units
|
| 2. |
Re-name units of length in metres and centimetres
Example 1: 125 cm = 1m 25cm
Example 2: 2m 3 cm = 203 cms
|
| 3. |
Solve and complete practical tasks and problems involving the
addition and subtraction of units of length (m and cm)
|
Strand Unit
Area
| 1. |
Estimate, compare and measure the area of regular and
irregular shapes
|
Strand Unit
Weight
| 1. |
Estimate, compare, measure and record the weight of a wide
variety of objects using appropriate metric units (kg and g)
Need to know: 1000g = 1kg
|
| 2. |
Solve and combine practical tasks and problems involving the
addition and subtraction of units of weight (kg and g)
Do not combine kg and g in same sum
|
Strand Unit
Capacity
| 1. |
Estimate, compare, measure and record the capacity of a wide
variety of objects using appropriate metric units (litres, 250ml and 500ml).
|
| 2. |
Solve and complete practical tasks and problem involving the
addition and subtraction of units of capacity,
Do not combine litres and ml
|
Strand Unit
Time
| 1. |
Consolidate and develop a sense of time passing
|
| 2. |
Read time in five minute intervals on analogue and digital
clocks
|
| 3. |
Read time in analogue and digital forms
|
| 4. |
Read and interpret simple time tables
|
| 5. |
Rename minutes as hours and minutes
Example: 70 minutes = ?
Restrict to 1 hr 55 minutes
|
| 6. |
Read dates from calendars and express weeks as days and vice
versa
|
| 7. |
Solve and complete practical tasks and problems involving
time.
|
Money
| 1. |
Rename amounts of money as pounds or pence and record using p
or £ symbol and decimal point.
|
| 2. |
Solve and complete one step problems and tasks involving the
addition and subtraction of money.
|
Representing and interpreting data
Data
| 1. |
Collect, organise and represent data using pictograms, block
graphs and bar charts
|
| 2. |
Read and interpret tables, pictograms, block graphs and bar
charts
|
| 3. |
Use data sets to solve and complete practical tasks and
problems
|
Chance
| 1. |
Use vocabulary of uncertainty and chance: possible,
impossible, might, certain, not sure.
|
| 2. |
Order events in terms of likelihood of occurrence.
|
| 3. |
Identify and record outcomes of simple random
processes.
|
Note on Informal Assessment / Teaching Strategies
| 1. |
Estimate when doing addition and subtraction
|
| 2. |
Drills in addition and subtraction – 3+ 6; 3 +16; 3 +
26;
|
| 3. |
Orally
solve word problems – single step, multi-step
|
| 4. |
Evaluate and review problem solving strategies
Read each problem three times – there are 402 cattle in
3 fields. 86 in field 1, 86 in field 2, how many in field 3? Draw and discuss
|
| 5. |
Teach concept of multiplication as continuous addition
2+2 +2 +2 = 2 x 4
|
| 6. |
Know number facts to 100
|
| 7. |
Work involving 0
|
| 8. |
Develop concept of division as repeated subtraction
|
Contact Us
|