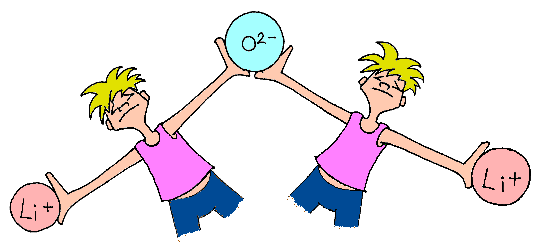
This is the force that binds electron and protons together in atoms and binds atoms and molecules together in ordinary matter. Electormagnetic forces also appear in the form of electrostatic force that acts between charged particles and magnetic forces that act between movingcharged particles It is the force on which all modern electric and electronic technology is based. This force can be attractive or repulsive. The distance over which this force can act is infinite. Its size is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the particles on which it acts (i.e. as the distance between the particles increases, the force decreases) Back to top
|

